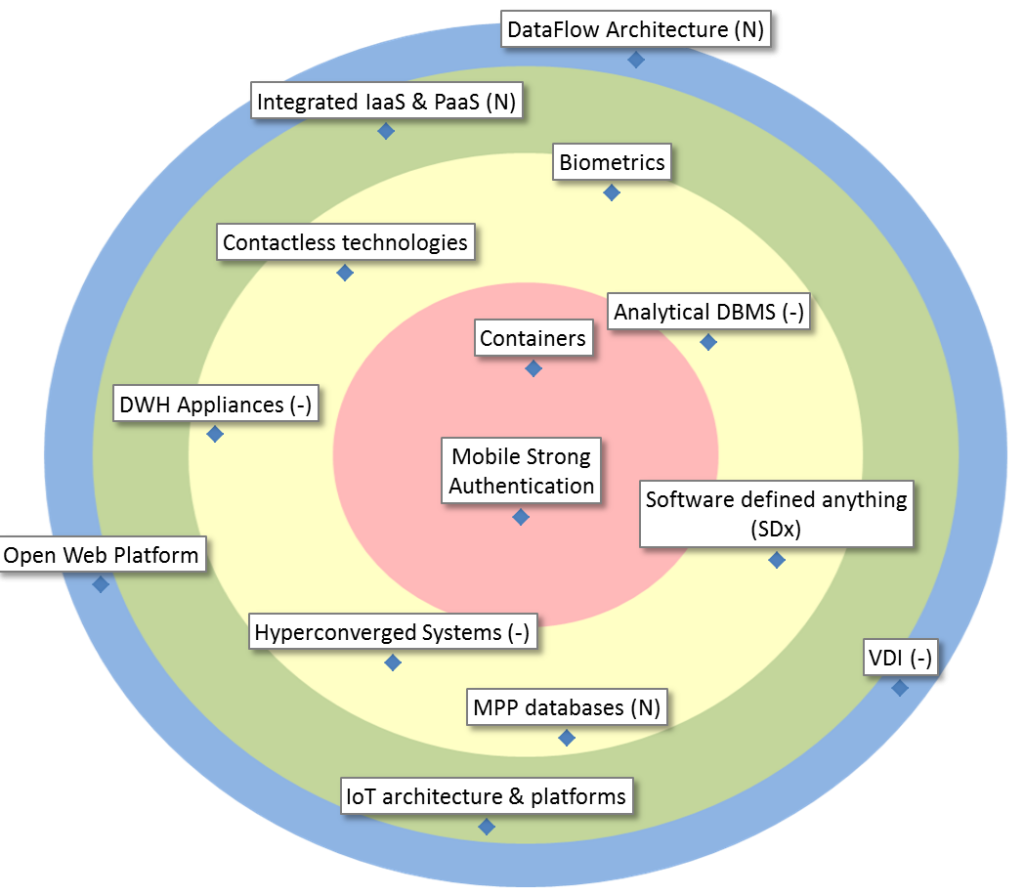
| Containers |
Containers are the new Cloud: They are lightweight virtualizations, using far less resources than typical virtual machines for nearly the same level of isolation. They’re also more ‘single-purpose’ and ‘throw-away’. They are used extensively to support applications on Cloud Platforms. |
| Mobile Strong Authentication |
As the eID is only partially compatible with smartphones and tablets, a different strong authentication mechanism is needed. Additionally, this alternative solution should be very user-friendly in a mobile context. |
| Analytical DBMS |
DBMS optimized for the execution of analytical queries (rather than transactions). The type may be Relational or NoSQL (Column-store, Key-Value, …). Many are able to execute advanced analytics algorithms in-database (cf. ‘Bring Compute to the Data’). |
| Biometrics |
Biometrics are metrics related to human characteristics (e.g. fingerprint, DNA, facial recognition). Biometrics authentication can be used as access control and finally finds acceptance as a strong authentication on mobile devices. |
| Contactless technologies |
Transmission technologies not requiring physical contact between transceivers, such as, NFC, RFID, Bluetooth Low Energy, and most techniques used in IoT devices. |
| DWH Appliances |
Machines (hardware + analytical DMBS + management software) that store, make available, and process large volumes of (relational) data with high availability, scalability, and performance. Designed for extreme ease of management, configuration and extension. |
| Hyperconverged Systems |
Storage, network & compute together in one system and controlled using software. Ideally suited to support Cloud Technology. |
| MPP databases |
Massively Parallel Processing databases. An MPP database is a database that is optimized to be processed in parallel for many operations to be performed by many processing units at a time. |
| Software defined anything (SDx) |
Instead of physical hard-wiring of system components, all infrastructure and platforms become virtualized, and configurable via software, enabling enormous flexibility in the datacenter. |
| Integrated IaaS & PaaS |
A current evolution within Cloud Technology is the convergence between the PaaS and IaaS models. The most feature-rich platforms of the near future will be able to offer a seamless transition between the capabilities of both Cloud delivery models. |
| IoT architecture & platforms |
These systems allow user-friendly management of IoT endpoints, and include dataflow control and security. |
| DataFlow Architecture |
The flow of (incoming) data, and not an application’s or cpu’s regular control flow, govern the architecture and runtime of a system. This an entirely new paradigm, even driven by new hardware, as opposed to the traditional way of working with fluxes. |
| Open Web Platform |
An ‘operating system’ for the Web, delivered as a set of foundational services upon which web applications can be built, delivered and used, purely on the Web. |
| VDI |
With virtual desktops, the desktop environment is separated from the physical devices in the office and run in the datacenter. VDI can be of interest in the context of telework/flex desk and disaster recovery. |